 |
| Figure 1. MFS2 Appearance
and Dimensions |
|
1. Definition
A Split-range transmitter is used to provide control (split-range control)
over 2 or more different elements using one input signal. For example,
in a heated swimming pool, the water temperature is the input signal and
the two controlled elements are hot and cold water supply valves.
Below figure 2 illustrates the MFS2 series’ selectable output characteristics,
V-shape or Parallel, depending on the user’s application requirements.
In the heated swimming pool example, user would select V-shaped characteristics
using the pool’s water temperature as the input signal, V1 as the
cold water supply valve control signal, and V2 as the hot water supply
valve control signal.
2. MFS2 Features and Functionality
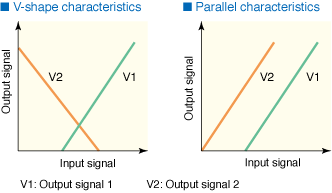 |
| Figure 2. V-shape Characteristics
and Parallel Characteristics |
The MFS2 is a split-range transmitter with 1 analog input and 4 analog
outputs available (See Figure 3 for a block diagram of the MFS2). The
unit is capable of using 1 input signal to control 4 different elements.
In addition to controlling the hot and cold water supply valves, in the
aforementioned example, by utilizing the isolation feature between input
and output, the MFS2 could also be used for the pool’s water temperature
monitoring (limit alarm instrument), and for the display of the pool’s
water temperature (display instrument).
The MFS2 features allow users to set different I/O characteristics for
each of its 4 outputs.
From a safety instrumentation perspective, it also provides functionality
for setting upper and lower limit values for each output.
The MFS2 also has a contact input. This feature provides forced output
of a preset value in response to a contact input status of either closed
or open. This is beneficial in applications where it is necessary to force
0% output in emergency situations.
3. Simple PC-based
Configuration
The functionality described in this article can be configured easily using
the PC Configurator software (model: MFS2CFG)*.
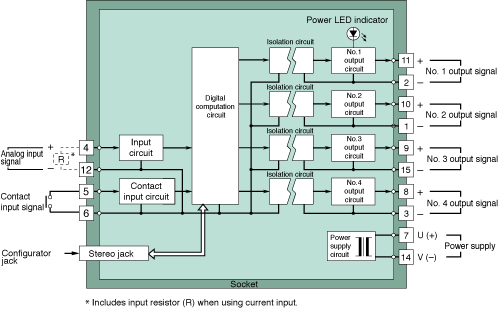 |
| Figure 3. MFS2 Block Diagram |
| |
The following settings are available for each output channel:
- Two sets of coordinates setting input to output characteristics
- Upper and lower limit values
- Selection of whether to use contact input (“Use”) or not
(“No Use”)
- Selection of forced output at contact closed or contact open
- Output value for forced output
Customers can easily accommodate changes in applications by modifying
these settings.
Figure 4 provides a specific setting example using the following values:
I/O characteristics: 0% output at 25% input and 100% output at 50%
input
Upper/lower limit values: Upper limit of 75% and lower limit of 30%
Forced output: Forced output of 40% when the contact closed
4. Graph-based Confirmation of Settings
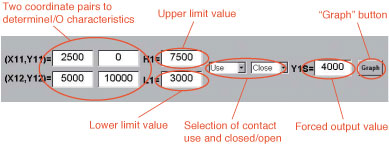 |
| Figure 4. Example Settings |
| |
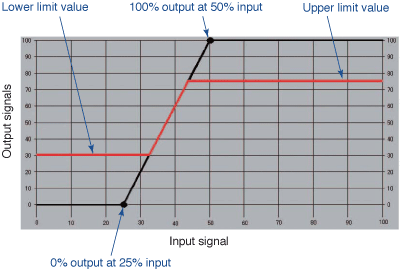 |
| Figure 5. Confirmation
Graph Display Screen |
Current settings of configured parameters can be easily confirmed by clicking
“Graph” button (see Figure 4).
Figure 5 displays the Figure 4 settings in graph form.
Black circles on the graph indicate coordinates that determine input
to output characteristics.
With the upper and lower limit values applied, the red line indicates
the input to output characteristics.
Note: A dedicated PC Configurator cable (Model: MCN-CON) is required to connect the MFS2 to user’s computer. |