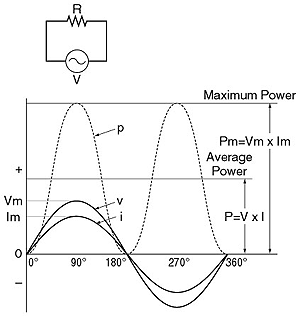
 |
An instantaneous value of a pure resistance circuit
and waveforms are shown in the figure (above).
p = vi
where, v = instantaneous voltage, I = instantaneous current. A maximum
power (Pm) is calculated by;
Pm = Vm x Im
where, Vm and Im are the peak value of the voltage and the current,
respectively. An average power is Pm/2. Therefore, we obtain
P = Pm / 2 = (Vm x Im) / 2 = Vm / 1.4142 x Im / 1.4142 = V x
I. |
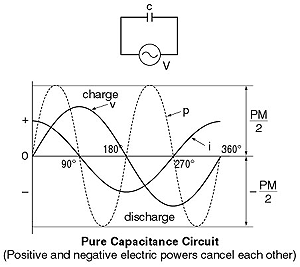 |
| This indicates that the power can be calculated by
using the same formula of a DC circuit when we use the effective value
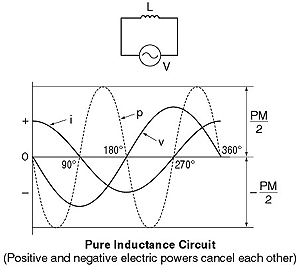
of the current and the voltage. Examples of a pure capacitance circuit
and a pure inductance circuit are shown the left. There is no consumption
of electric power. (In actual circuits, there is some consumption
of electric power since a capacitor and an inductor have some resistance
associated with them.) Positive electric power and negative electric
power cancel each other, and the total power becomes 0 watt. |
 |
|
 What
is the electric power in an electric circuit with a pure resistance?
What
is the electric power in an electric circuit with a pure resistance?
